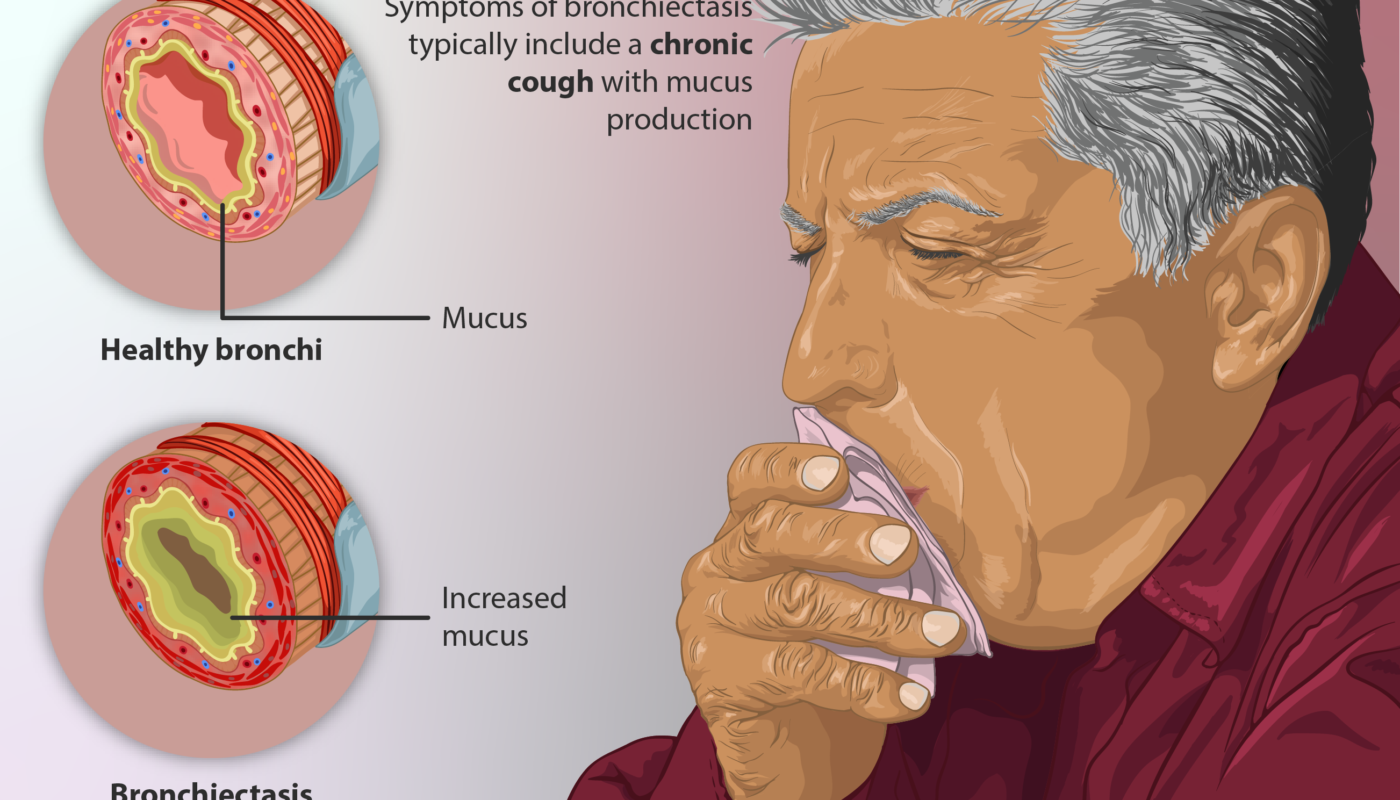
Bronchiectasis is a chronic lung condition characterized by damaged and widened airways in the lungs. As the airways become dilated, it becomes difficult to clear mucus and phlegm from the lungs, leading to persistent infections. While there is no cure for bronchiectasis, treatment aims to manage symptoms, stop progression of disease and prevent infections.
Antibiotics
As the name suggests, antibiotics are the mainstay of treatment for bronchiectasis as they help control and prevent infections. Antibiotics are prescribed depending on the type of bacteria found in sputum cultures. Common antibiotics include:
Macrolides: Macrolide antibiotics like azithromycin and erythromycin are frequently prescribed long-term for their anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects in addition to antibacterial activity. They help reduce exacerbations and improve quality of life in patients with bronchiectasis.
Quinolones: Fluoroquinolones like ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin are broad spectrum antibiotics used for 4-12 weeks during exacerbations. In cases where cultures show multi-drug resistant pathogens, newer quinolones are prescribed.
Cephalosporins: Oral cephalosporins like cefuroxime are used short-term during exacerbations. Intravenous cephalosporins are administered in hospital for severe exacerbations or when oral route is not feasible.
Other antibiotics: Other antibiotics prescribed include co-trimoxazole, doxycycline and amoxicillin-clavulanic acid depending on sputum culture sensitivity reports and severity of infections. Care must be taken to prevent development of drug resistance with long-term use.
Airway Clearance Techniques
Physiotherapy plays an important supporting role in Bronchiectasis management. Airway clearance techniques help remove excess mucus from the lungs and improve airflow. Commonly used techniques include:
Chest Physiotherapy: Manual techniques like postural drainage, cupping and clapping performed with a physiotherapist are effective in mobilizing mucus.
Airway Clearance Devices: Oscillating devices like the Flutter and active cycle of breathing technique help clear mucus with controlled breathing maneuvers.
Hypertonic Saline: Inhaling 3% saline using a nebulizer hydrates the mucus and loosens secretions for easier removal.
Mucolytic Drugs
Mucolytic drugs help thin mucus secretions and enable easier clearing. Commonly used mucolytics include:
N-acetylcysteine: An over-the-counter mucolytic with antioxidant properties, NAC shows promise in reducing exacerbations when used long-term.
Hypertonic saline: As mentioned earlier, inhaling 3% saline solution acts as a mucolytic by providing hydration.
DNAse: Recombinant human DNase or pulmozyme is an inhaled medication that cleaves DNA strands present in mucus secretions, reducing its viscoelasticity.
Anti-inflammatory Drugs
Chronic inflammation plays a critical role in bronchiectasis disease progression. Immunomodulators help control inflammation:
Inhaled Corticosteroids (ICS): ICS like budesonide and beclomethasone reduce inflammation within airways and lung parenchyma in mild to moderate disease.
Macrolide Antibiotics: Besides antibacterial effects, long-term macrolide therapy reduces inflammation through immunomodulation.
Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists: Montelukast suppresses leukotriene mediated inflammation and is beneficial as add-on therapy.
While bronchiectasis has no cure, proper long-term management can effectively control symptoms and prevent disease progression. A combination of airway clearance, antibiotics, mucolytics and anti-inflammatories is often required depending on individual patient factors. With close monitoring and compliance to treatment plans, patients can achieve optimal bronchiectasis control and lung health.