The demand for plastic packaging and films has increased exponentially but most plastics take centuries to decompose in landfills and oceans. There is a growing need to find sustainable alternatives to replace petroleum-based plastic films. One such promising alternative is cellulose films which are made from renewable plant fibers and are completely biodegradable and compostable.
What are Cellulose Films?
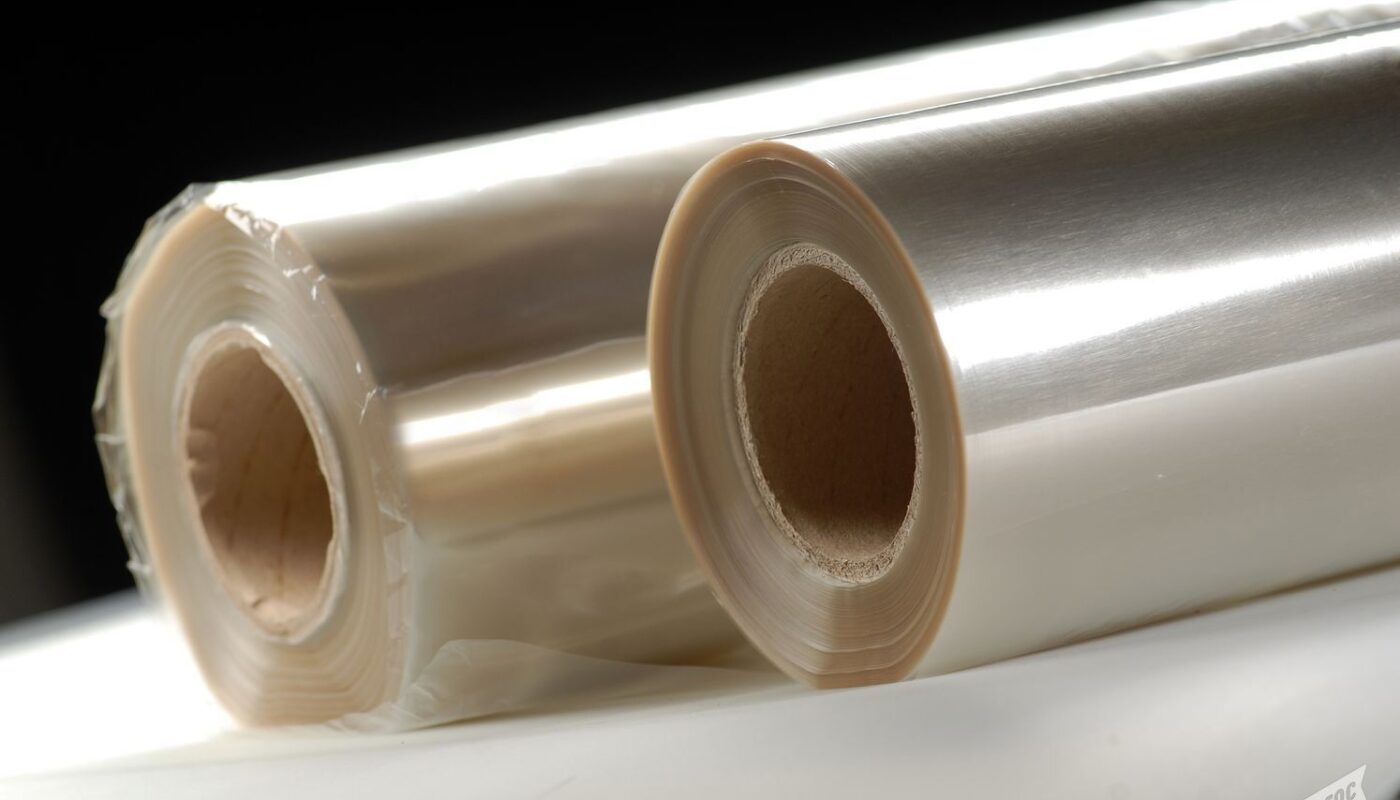
Cellulose films are thin plastic-like films made primarily from regenerated cellulose obtained from renewable plant sources like wood pulp and cotton linter. Cellulose is the most abundant organic polymer on Earth and forms the basic structural component of the primary cell wall of green plants. The cellulose is purified, dissolved and then reconstituted as films through an environmentally friendly process. The resulting films have properties very similar to conventional plastic films but offer sustainability advantages.
Physical Properties of Cellulose Films
Cellulose films closely mimic the physical properties of petroleum-based plastic films like polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polystyrene (PS), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), etc. They are transparent, odorless, colorless, glossy, stiff yet flexible films with high tensile strength. Their water vapor and gas permeability is also comparable to conventional films. This allows cellulose films to seamlessly replace plastics in various packaging applications without compromising on functionality or performance.
Biodegradability and Compostability
Unlike plastic films that persist in the environment for centuries, cellulose films are completely biodegradable and compostable. They can break down into carbon dioxide, water, and organic matter within 180 days when exposed to microbial activity in industrial composting facilities or natural environments like soil and marine water. This means that at the end of their useful life, cellulose films do not end up as litter or pollute the environment like plastic but safely return to nature.
Applications of Cellulose Films
Given their properties equivalent to plastic yet sustainability advantages, cellulose films are increasingly being adopted across industries as eco-friendly replacements for plastic packaging films:
Food Packaging
Cellulose films are widely used to package snacks, dry foods, coffee, fruits and vegetables. They act as moisture barrier and seal films for food containers, bags, pouches and wraps. Being compostable, they pose no environmental threat at end-of-life.
Pharmaceutical Packaging
Many pharmaceutical blister packs and medical device packaging now use cellulose films for their promised stability, printability and compliance with medical waste regulations when disposed.
Home and Personal Care Product Packaging
Shampoo, lotion, cosmetic and toiletries packaging leverages Cellulose Films for their ability to provide barrier protection along with sustainable disposal options.
Industrial and Agricultural Films
Stretch wrap, pallet wrap, mulch films used in agriculture are moving to cellulose variants due to their eco-friendly profile. They keep products secure during transit and storage.
Barriers to Widespread Adoption
While cellulose films offer tremendous sustainability benefits over plastic, a few barriers currently limit their mass adoption:
Higher Material Cost:
Being manufactured from plant fibers through multistep processes, cellulose films are still more expensive than most petroleum-based plastics.
Supply Chain Limitations:
The cellulose industry is smaller compared to petroleum plastics. However production capacities are improving to meet demand.
Limited Film Thickness Range:
Cellulose films are mainly available in the thickness range of 10-80 microns while plastics can be extruded to thicknesses up to several millimeters.
Moisture Sensitivity:
Cellulose films require dry packing and storage to retain properties as they can absorb moisture over time.
Compatibility with Machinery:
Equipment used to process plastic films often requires modification to accommodate cellulose variants.
The good news is that targeted R&D investments, innovative partnerships and supportive government policies are steadily addressing these challenges and cellulose films are projected to contribute significantly to the global transition from plastics to sustainability. Multiple studies also show their use leading to lower carbon footprint over the product lifecycle compared to plastics.
With plastic pollution emerging as one of the most pressing worldwide environmental crises, there is a compelling need for alternatives that are renewable, biodegradable and aligned with the principles of responsible consumption and circular economy. Cellulose films exhibit strong potential in this regard and their adoption across industries is likely to accelerate in the coming years. Combined with efforts towards plastic waste reduction and recycling, cellulose films can play an invaluable role in combating plastic pollution and encouraging sustainability.
Note:
1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research
2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it