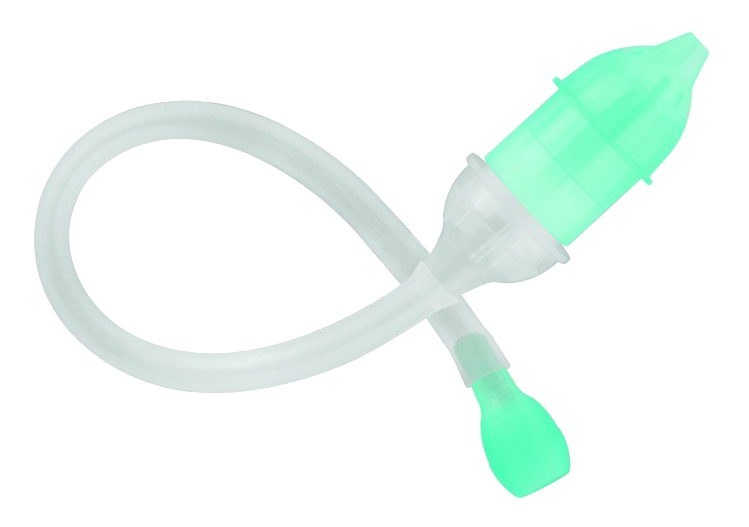
What is an Ultrasonic Aspirator?
An ultrasonic aspirator is a surgical instrument used to fragment and remove tissues during operations. It works using high-frequency ultrasonic vibrations generated from a transducer at the tip of the instrument. When this vibrating tip is placed against tissue, it produces localized cavitation bubbles which help break up and emulsify tissues. At the same time, the device also works as an aspirator, drawing tissue debris and bodily fluids away via suction through a tube connected to it.
Applications in Surgery
Ultrasonic aspirators have various useful applications in surgical procedures:
– Neurosurgery: It is widely used in brain and spine surgeries for tasks like removing tumors, cysts, blood clots, and scar tissues very precisely without damaging nearby delicate nerves and vessels. The fine control and precise cutting ability help achieve optimal resection.
– Orthopedic Surgery: In orthopedics, ultrasonic aspirators aid in removing cartilage, bone spurs, and osteophytes with minimal blood loss and less trauma to surrounding tissues compared to mechanical cutting or grinding tools.
– ENT Surgery: ENT surgeons routinely use Ultrasonic Aspirators for tasks like sinus surgery, removal of nasal polyps and nasal packing, and trimming of turbinates for better breathing. It provides improved visibility and access in congested sinus cavities.
– General Surgery: It can efficiently and safely remove tough tissues and abscesses in procedures like thyroidectomy, laparoscopic surgeries, and incision/drainage of abscesses. Its pooling effects help drain pus, exudates, and infectious materials effectively.
– Dental Surgery: Dental ultrasonic aspirators aid in procedures like root canal treatment, periodontal surgery, removal of cysts, and osteoplasty for dental implant placement. It protects delicate tooth structures and alveolar bone.
Advantages Over Traditional Methods
The key advantages of ultrasonic aspirators compared to conventional surgical instruments like scalpels, electrocautery devices, and rongeurs include:
– Greater Precision and Control: The ability to precisely emulsify tissues with minimal blood loss or trauma to surrounding structures helps achieve optimal tumor resection and hemostasis.
– Improved Vision and Access: Its aspirating capability creates a clear surgical field by removing fluids, blood, debris continuously, enhancing visualization especially in limited access sites.
– Minimal Thermal Damage: Unlike electrocautery, ultrasonic energy causes negligible collateral thermal damage to surrounding tissues as the tip never gets heated during use.
– Less Operative Time: Ultrasonication allows for faster removal of both soft and hard tissues in a single instrument than piecemeal resection with multiple traditional tools, reducing procedure time.
– Less Post-operative Pain and Bleeding: Precisely ablating tissues with minimal surrounding trauma reduces post-op complications like pain, swelling, and blood loss for patients compared to other methods.
Advancements in Technology
In recent years, newer ultrasonic aspirator models integrate advanced technologies:
– Digital Drive Electronics: Microprocessor-controlled power delivery provides adjustable variable ultrasound intensity and aspiration levels through digital controls.
– Lighted Tips: Fiber optic illuminated tips with integrated light cables enhance visualization in poorly lit anatomical areas deep inside the body.
– Irrigation Facility: Ability to deliver saline or other irrigating liquids to the tip aids washing away debris and maintains a clear field continuously.
– Integrated Suction: Newer systems integrate more powerful suction capabilities with higher flow rates to rapidly remove emulsified tissues and fluids.
– Sterilizable Design: Most modern devices feature fully immersible handpieces and components that can be sterilized for repeated use, reducing maintenance costs.
Future Scope
With ongoing improvements, surgeons expect ultrasonic aspirators to play an even greater role in various minimally invasive procedures in future. Researchers are also working on:
– Integrating ultrasound imaging capability for precise real-time visualization of ablation zones.
– Developing 3D-printed aspiration tips customized for specific anatomies to optimize resection.
– Exploring robotics integration to enable their remote operation through robotic arms for improved ergonomics.
– Combining ultrasonic energy with cold plasma technology or laser for synergistic tissue effects.
In conclusion, ultrasonic aspirators have established themselves as a vital surgical tool due to their safe and precise tissue removal ability. Modern advances will further strengthen their utility across diverse specialties.
*Note:
1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research
2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it.